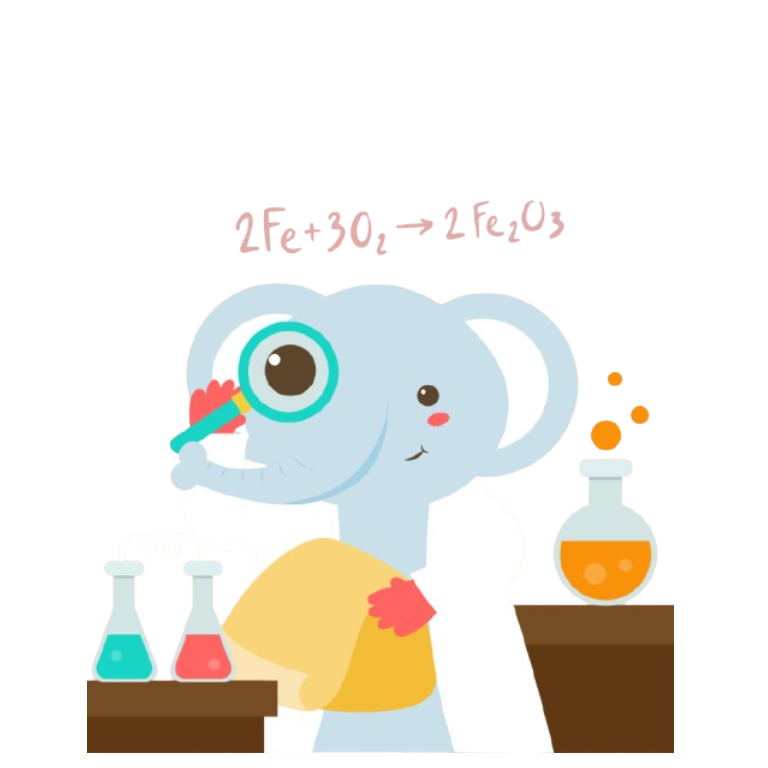
Endothermic Reaction
Ammonium Nitrate + Water: A Cooling Reaction
Observe the endothermic reaction when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, absorbing heat from the surroundings. Watch the temperature drop as the reaction proceeds!
Water Only
Temperature: 25°C (Room Temp)
0°C
25°C
50°C
Observation:
Pure water at room temperature. The thermometer shows 25°C.
The Science Behind Endothermic Reactions
Chemical Reaction:
When ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, it absorbs heat from the surroundings:
NH₄NO₃(s) + H₂O(l) → NH₄⁺(aq) + NO₃⁻(aq)
This process is endothermic (ΔH > 0), meaning it requires energy to proceed.
Key Concepts:
- Endothermic reactions absorb heat from their surroundings
- Enthalpy change (ΔH) is positive for endothermic processes
- Dissolution energy is required to break ionic bonds in the crystal lattice
- Temperature drop occurs because heat energy is absorbed by the reaction
Real-world Applications:
Ammonium nitrate is used in instant cold packs for sports injuries. When the salt dissolves in water inside the pack, it creates a cooling effect.