Flower Dissection
Explore the reproductive anatomy of a flower. This virtual dissection exercise allows you to identify and learn the functions of the different floral parts without the need for physical specimens.
Help & Instructions
▼- Identify the Parts: Click on the different flower parts to reveal their names and functions.
- Dissection Challenge: Follow the instructions to "dissect" the flower by selecting parts in the correct order.
- Quiz Challenge: Answer questions about flower anatomy and reproduction.
- Identify the male and female reproductive parts of a flower.
- Describe the function of each floral part (e.g., petals, sepals, stamen, pistil).
- Understand the process of pollination and fertilization.
Virtual Dissection: Identify the Parts
Click on the different parts of the flower to learn about them.
Quiz Challenge: Flower Anatomy
Which part of the flower attracts pollinators with its color and scent?
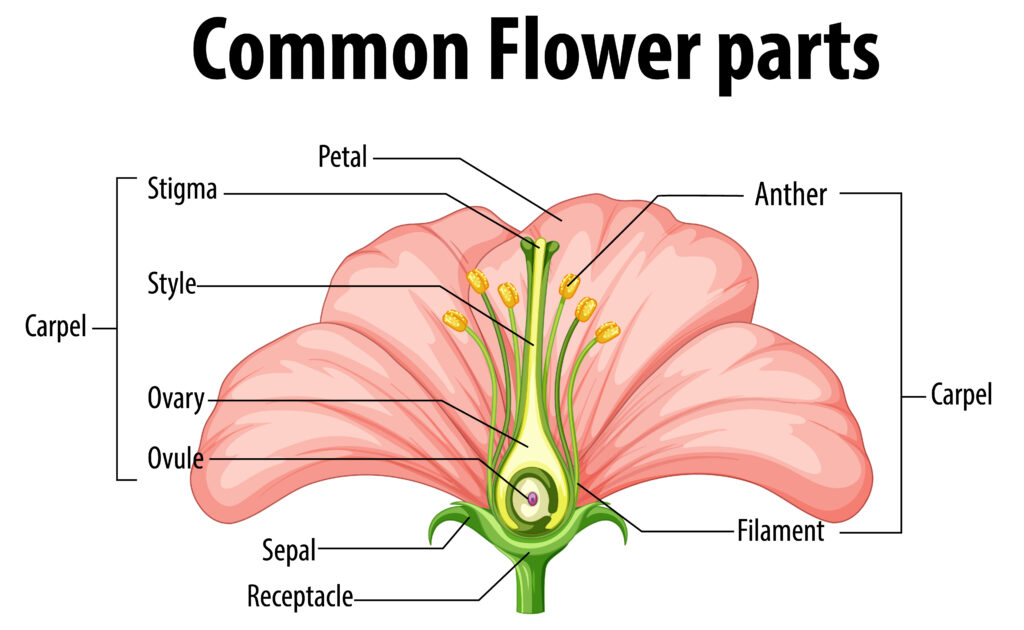
Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants (angiosperms). Their anatomy is fascinating, with each part playing a crucial role in the process of sexual reproduction. The main parts are arranged in four concentric whorls on a receptacle. Understanding these parts is fundamental to understanding plant biology.
The Major Parts of a Flower
The **stamen** is the male reproductive organ, composed of the **anther** and **filament**. The anther produces pollen grains (male gametes), and the filament supports the anther.
The **pistil** (or carpel) is the female reproductive organ, typically composed of the **stigma**, **style**, and **ovary**. The stigma receives pollen, the style is a tube connecting the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary contains the ovules (female gametes).
The **petals** are often brightly colored to attract pollinators. The **sepals** are the leaf-like structures that protect the developing flower bud.