Pollen Grain Mount & Germination
Explore the fascinating world of pollen grains - their structure, preparation for microscopic observation, and the germination process. Develop your understanding of plant reproduction through interactive activities.
Help & Instructions
▼- Pollen Germination: Observe pollen grains and their germination process under the virtual microscope
- Mount Preparation: Learn the correct sequence for preparing a pollen grain mount
- Quiz: Test your knowledge with interactive questions
- Use the hint button if you need help with any activity
- Understand the structure of pollen grains
- Learn the process of pollen germination
- Master the technique of preparing a pollen mount
- Identify factors affecting pollen germination
Pollen Germination Observation
Observe pollen grains and their germination process under the virtual microscope.
Pollen Mount Preparation
Arrange the steps in the correct sequence for preparing a pollen grain mount.
Pollen Knowledge Quiz
Test your understanding of pollen grains and germination.
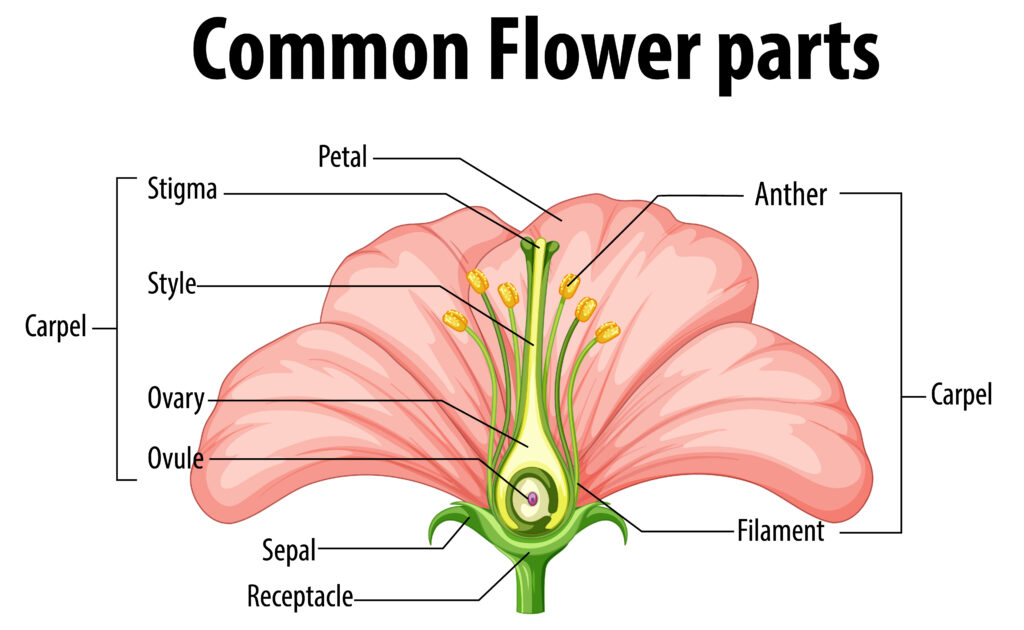
Pollen grains are male gametophytes of seed plants, containing the male gametes. They have a tough outer wall called the exine, which is resistant to decay and contains unique patterns that help in species identification. The inner wall is called the intine. When pollen lands on a compatible stigma, it germinates to produce a pollen tube through which sperm cells travel to fertilize the ovule.
The Biology of Pollen
Pollen grains have a complex structure:
- Exine: The outer, durable layer made of sporopollenin
- Intine: The inner layer made of cellulose and pectin
- Germination Pore: Area where the pollen tube emerges
- Generative Cell: Divides to form two sperm cells
- Vegetative Cell: Controls the growth of the pollen tube
Pollen germination involves several steps:
- Hydration of the pollen grain on the stigma
- Activation of metabolic processes
- Emergence of the pollen tube through the germination pore
- Growth of the pollen tube through the style toward the ovule
- Release of sperm cells for fertilization
Several factors influence pollen germination:
- Temperature: Optimal range is typically 20-30°C
- Humidity: High humidity favors germination
- Sugar Concentration: Provides energy for tube growth
- pH: Slightly acidic to neutral pH is optimal
- Compatibility: Must match with the stigma of the same species